CDC 전문가: 기존 COVID-19 백신은 여전히 오미크론 바이러스에 효과적입니다
2021-12-01

새로운 코로나 바이러스는 새로운 돌연변이 균주를 재현합니다 “오미 크론”. 11 월 현재 28, 남아프리카, 이스라엘, 벨기에, 이탈리아, 영국, 오스트리아, 그리고 홍콩, 중국, 이 돌연변이 균주의 입력을 모니터링했습니다. 이 돌연변이 균주의 입력은 우리나라의 다른 지방과 도시에서 발견되지 않았습니다.. Many countries have upgraded their anti-epidemic measures to close the borders, restrict travel, and ban flights. Is “오미 크론” getting closer and closer to us? How should we guard against it?
Is “오미 크론” very close to us?
Xu Wenbo, Director of the Institute of Viral Disease Prevention and Control of the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention: “오미 크론” mutant strains are spreading rapidly with global transportation. 사실로, not only Omicron, but any strain that is infected can be quickly imported to other countries by aircraft. Whether the propagation speed of “오미 크론” will increase is still unknown and requires observation and research in the coming weeks. But it is very close to us, because China and many countries have air flights. NS “오미 크론” strain is not only in Africa, but has been imported into other countries, and it may have a potential epidemic in some countries, so The opportunity to import into China is great.
How dangerous is “오미 크론”?
Xu Wenbo: The amino acid mutation sites of the spike protein on the “오미 크론” include the “델타” 바이러스, 그리고 “Alpha”, “Beta” 그리고 “델타” viruses some important amino acid mutation sites. but the increase in mutation sites does not necessarily mean that its transmission is enhanced, nor does it mean that its immune escape is necessarily stronger than that of the “델타” 바이러스. Aggregation mutations are not necessarily an accumulation, 그리고 1+1 is greater than 2 In that form, structural virology, cross-immunization and neutralization, and field epidemiology are needed to observe the protective effect of the vaccine. 일반적으로 말하면, “오미 크론” is still a new crown virus, and it will not undergo subversive changes.
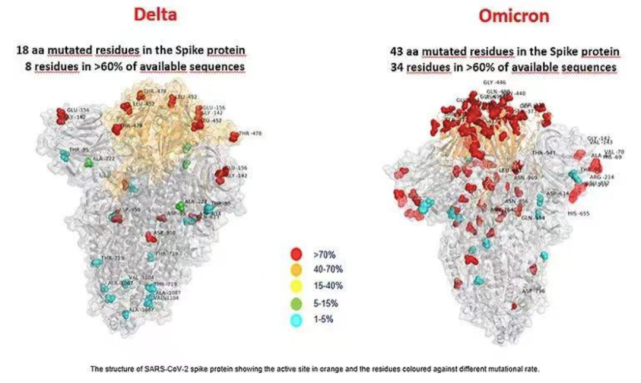
Does “오미 크론” affect our country’s existing nucleic acid detection reagents?
Xu Wenbo: The mutations of “오미 크론” are mainly concentrated on the neutralizing antigen spike protein. The mainstream nucleic acid detection reagents in China are designed for ORF/ab gene and N gene. The two genes seem to have not changed, so the sensitivity and specificity are not affected. The mainstream nucleic acid detection reagents in China can deal with the input of the “오미 크론” mutant strain.
What impact does “오미 크론” have on the vaccine?
Xu Wenbo: “오미 크론” is still a new coronavirus. Although its amino acids are cumulatively mutated, the vaccine is still effective and can reduce the proportion of severe illness and death. It cannot completely break through immunity. Barrier, because in addition to antibody immunity, there is also T cell immunity, and our country has a variety of vaccine immunization technology routes on the market, including inactivated vaccines, protein vaccines, vector adenovirus vaccines, as well as booster injections, sequential immunization, and then there is also the development of second-generation vaccines, which can deal with the “오미 크론” strain.
What should scientists pay attention to when observing “오미 크론”?
Xu Wenbo: As a scientist, we should pay attention to the following points: 1. Whether the mutation of “오미 크론” lead to increased transmission and whether it will exceed the “델타” 바이러스 . 2. How strong is the immune escape ability of “오미 크론”. 3. How did “오미 크론” come into being.
How does our country respond to the import of “오미 크론”?
Xu Wenbo: Our country’s existing COVID-19 prevention and control policies, “foreign import prevention” 그리고 “internal prevention rebound”, conduct detailed epidemiological and genomic monitoring of all imported cases. It is possible to stop the spread of “오미 크론”.
일상생활에서, 공공은 어떻게 “오미 크론”?
Xu Wenbo: 1. 일반인은 마스크 착용과 사회적 거리두기 준수, 특히 건강 모니터링. 새로운 관상 동맥 폐렴의 증상이 의심되는 경우, 체온을 제때에 모니터링하고 주도적으로 의사를 만나야 합니다.. 2. 불필요한 출구 줄이기, 특히 국가에 “오미 크론” 균주가 의심되거나 만연하거나 수입된 경우.
원천: CCTV 뉴스
















