マスクをエチレンオキシドで滅菌する必要があるのはなぜですか (それは)?
2022-01-17
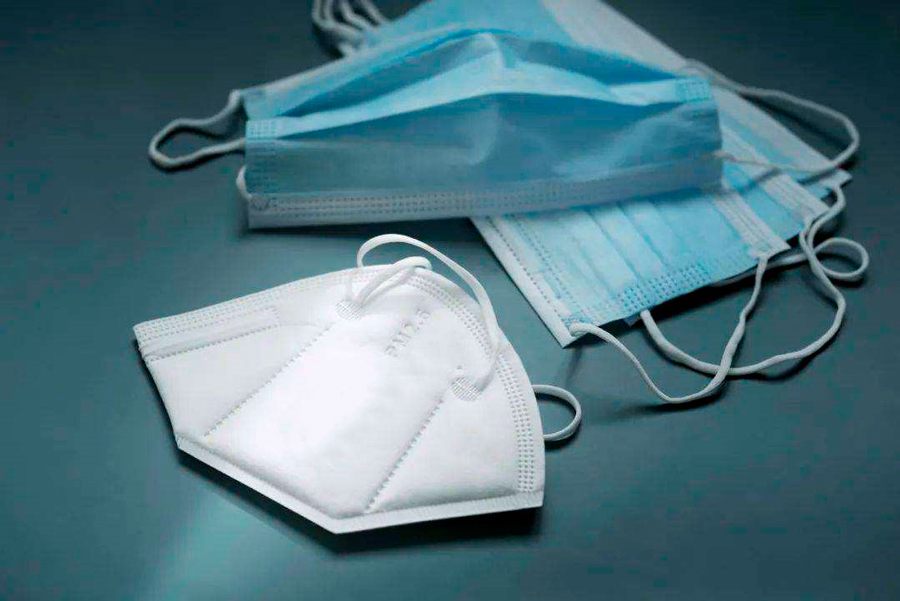
NS マスク on the market are basically divided into three categories: 民間マスク, 医療用マスクと専門的な呼吸保護マスク.
民間マスク, 使い捨て介護マスクなど. 主に、ほとんどの人々の日常生活や仕事のニーズを満たす日常用保護マスクを指します。.
医療用マスクは医療用保護マスクに分けられます (N95マスク), medical surgical masks and disposable medical masks.
① Medical protective masks (N95マスク) are suitable for the protection of medical personnel and related staff against airborne respiratory infectious diseases.
② Medical surgical masks are suitable for basic protection of medical personnel or related personnel, as well as protection against the spread of bodily fluids and splashes during invasive operations.
③ Disposable medical masks are suitable for the wearer’s hygiene care in a general medical environment where there is no risk of body fluids and splashing.
Professional protective masks, such as particulate protective masks KN95. Protects against all types of particulate matter, including dust, 煙, mist and microorganisms.
What is the difference between sterilized masks and non-sterile masks?
Masks that have undergone sterilization methods such as ethylene oxide (それは) are called sterilization-grade masks [4] (the outer packaging needs to be marked with sterilization grade). Unsterilized products will be marked on the outer packaging as non-sterile grade, common grade, 等.
In medical places that strictly control the microbial environment (such as ICU, operating room, NS。), all the items entering must meet sterility standards, so sterilization-grade medical masks are required. In places with sterility requirements, sterilization-grade masks are usually used. But in ordinary occasions, both ordinary grade and sterilization grade can be used.
The sterilization method of mask products is usually ethylene oxide (それは). The penetrating force is very strong, which can achieve the effect of effective sterilization without damaging the items. The principle is to cause the death of microorganisms through a series of chemical reactions [2], so as to achieve the sterilization effect.
















